Beijing has more than enough
sights to keep the average visitor busy, but after traveling all this
way, it would be a shame not to grasp the opportunity to get out of the
city. Of course, the Great Wall is an absolute must, but not far from
the city are also ancient temples nestled on green hillsides and the
vast necropolises of the Ming and Qing emperors. To the southwest is the
300-year-old stone Marco Polo Bridge and neighboring Wanping, a rare
surviving example of a walled city. Both are an easy suburban bus ride
from the city. Otherwise, most Beijing hotels organize tours to these
sights.
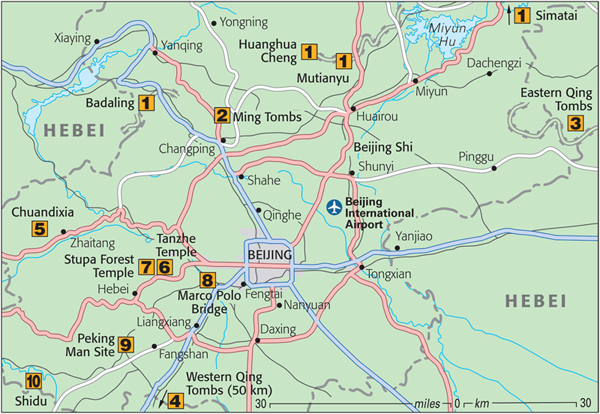
Top 10 Sights
-
Great Wall
A
visit to the wall is an absolute must. The closest section to Beijing
is at Badaling, and you can get there and back in half a day. However,
if you suspect that your appreciation of this matchless monument would
be improved by the absence of coach-loads of fellow tourists, then
considering traveling that little bit farther to the sites at Mutianyu,
Huanghua Cheng, and Simatai .

The Great Wall, snaking over high ridges north of Beijing
-
Ming Tombs
The
Ming Tombs are the resting place for 13 of the 16 Ming emperors. These
are Confucian shrines and follow a standard layout of a main gate
leading to a series of courtyards and a main hall, with a “soul tower”
and burial mound beyond. The tombs are not as colorful and elaborate as
Buddhist and Daoist structures, and only three have been restored and
are open to the public, however the necropolis is definitely a
worthwhile stop-off as part of an excursion to the Great Wall .

Great Palace Gate, Ming Tombs

Spirit Way at the Ming Tombs

Spirit Tower, Ming Tombs
-
Eastern Qing Tombs
The
remoteness of the Eastern Qing Tombs, over the border in Hebei
province, makes them far less popular than their Ming counterparts,
despite the fact that the setting is even more splendid. In fact, the
Eastern Qing Tombs make up the largest and most complete imperial
cemetery in China, built on a scale as grand as the Forbidden City. Of
the many tombs here, only five are the burial places of Qing emperors,
but there are also 14 empresses, and 136 imperial consorts. Notable are
the tomb of the Qianlong Emperor, with an incredible tomb chamber
adorned with Buddhist carvings, and the lavish tomb of the devious Empress Cixi. -
Western Qing Tombs
If
few tourists ever visit the Eastern Qing Tombs, fewer still make it out
here to their equally distant western counterparts. This vast burial
complex comprises over 70 tombs in all, set in spectacular surroundings.
Tombs include those of the emperors Daoguang, Guangxu, Jiaqing, and
Yongzheng (r. 1723–35). It was the latter who founded this particular
necropolis, perhaps because he could not bear to be buried beside his
father, whose will he had thwarted when he seized the throne from his
brother, the nominated heir. Also here, in a nearby commercial cemetery,
are the remains of Pu Yi, the last emperor of China . -
Chuandixia
On a steep mountainside, Chuandixia is a crumbling but picturesque hamlet of courtyard houses (siheyuan),
most dating from the Ming and Qing dynasties. An entry ticket allows
access to the entire village, all of which can be explored in a few
hours. The population consists of about 70 people spread over a handful
of families. Accommodation with one of the families can be provided for
those wanting an experience of rural hospitality.

Chuandixia village
-
Tanzhe Temple
This
enormous temple dates back to the 3rd century AD, when it was known as
Jiafu Si. It was later renamed for the adjacent mountain, Tanzhe Shan.
It has a splendid mountainside setting, and its halls rise up the steep
incline. The temple is especially famous for its ancient trees. There
are no restaurants in the area, so bring your own lunch. -
Stupa Forest Temple
Near
the parking lot for the Tanzhe Temple is this even more fascinating
temple, notable for its marvelous collection of brick stupas hidden
among the foliage. Each stupa was constructed in memory of a renowned
monk. The towering edifices were built in a variety of designs, and the
earliest among them dates from the Jin dynasty (1115–1234).-
28 miles (45 km) W of Beijing
-
6086 2505
-
Subway to Pingguo Yuan (1 hr), then bus 931 or tourist bus 7
-
8am–5pm daily

Stupa Forest Temple
-
-
Marco Polo Bridge
Straddling
the Yongding River near Wanping town, the 876-ft (267-m) marble bridge
was first built during the Jin dynasty in 1189 but was destroyed by a
flood. The current structure dates to 1698. The bridge acquired its name
when legendary voyager Marco Polo described it in his famous treatise The Travels.
The balustrades along the length of the bridge are decorated by more
than 400 stone lions, each one slightly different from all the others.
On July 7, 1937, the Japanese Imperial Army and Nationalist Chinese
soldiers exchanged fire at the bridge, an incident that led to the
Japanese occupation of Beijing and war.

Marco Polo Bridge
-
Peking Man Site (Zhoukoudian)
In
the 1920s, archeologists removed from a cave at Zhoukoudian some 40-odd
fossilized bones and primitive implements, which they identified as the
prehistoric remains of Peking Man. It was thought that this exciting
discovery provided the much sought-after link between Neanderthals and
modern humans. Designated a UNESCO World Heritage site, the area is
geared toward specialists, although the small museum has an interesting
collection of tools and bone fragments. Peking Man himself is not here –
his remains mysteriously disappeared during World War II. -
Shidu
Shidu
offers a fabulous escape from the commotion of urban Beijing and a
chance to enjoy some stunning natural scenery. Before the new road and
bridges were built, travelers had to cross the Juma River ten times as
they journeyed through the gorge between Shidu and nearby Zhangfang
village, hence the name Shidu, which means “Ten Crossings.” Pleasant
walking trails wind along the riverbank between impressive gorges and
limestone formations.